1. Lines are a maximum
of 80 characters long, identifiers are a maximum of 32 characters long.
2. Continuation lines
are signaled by an "&" as the last character of a line to be continued.
A command can be up to 1024 characters long.
3. Delimiters are comma,
slash, equal sign, or blank. (',' '/' '='' ').
The triplet: 1, 0, 0 refers to all points.
The triplet: 0, 0, 0 refers to the set of points defined in the last geometry command.
| signifies alternate choices
, or / separates parameters
___ underline specifies default
8. All names ( surface, region, pset,...) should be limited to 32 characters.
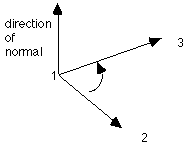
9. The right hand rule is used to determine normals to planes and to sheet surfaces. The first two points determin the first vector and the first and third point determine the second vector. By curling the fingers of the right hand from the first vector toward the second vector, the right thumb will point in the direction of the normal.
10. To separate commands on the same
line use a semicolon (;).
11. Three coordinate systems are
used.
rtz refers to a cylindrical coordinate system aligned along the z-axis, where r is the radius measured from the zaxis, t (theta) is the angle measured in the xy-plane from the positive x-axis toward the positive y-axis and z is the height measured from the xy-plane.
rtp refers to a spherical coordinate system, where r is the radius measured from the origin, p (phi) is the angle in the xy-plane measured from the positive x-axis toward the positive y-axis, t (theta) is the angle measured from the positive z-axis to the positive y axis.
